Airbnb Analysis
SAS Project - Airbnb Analysis
# Airbnb Analysis
Abstract:We first conducted an exploratory analysis of the data, then conducted relevant time series analysis, discovered quarterly changes in housing popularity, built multiple models for detailed regression analysis and testing, built a recommendation system based on the data, and, based on reviews, drew a word cloud diagram.
Keywords: EDA, time series analysis, regression, recommendation system
1. Exploratory Data Analysis
This section provides an overview of the project’s objective, which is to analyze data sourced from the provided dataset Airbnb,which outlines the key areas of analysis, including market distribution, factors influencing house prices, room popularity, factors affecting listing room acceptance, and also encapsulates the additional analyses performed to further understand the dynamics of the Airbnb market, particularly in the context of Sydney listings.
Market size relation analysis

The pie chart below show this information for market size in Sydney. Note that Sydney city area has the most proterty for booking. The top five are Sydney City, Waverley, Pittwater,Randwick, Warringah.
Room type relation analysis

Entire room/apt has the biggest market size in all 4 types of rooms.
But Does the rooms type really affect the number of booking?

It seems Entire home / apt have a much higher booking than other types of rooms.But let’s also see the ration of booking numbers to total market size of each roomtype.

Through the ratio of booking number and total number of their room type, hotel shows more popular, and shared room is not very popular. Entire home/apt has the most booking number just because the quantity of this room type in airbnb is the most available type.
Time relation series with listing and review number trend by room type

We assume the listing time is the first review time.Then we find:From 2014, the Markt size become rapidly expanding. Especially Entire home/apt and Private room.After covid-19 pandamics outbreak about 2020, all type of room new listings decrease greatly. After the epidemic, 2022 began to pick up translation.

From the chart, The outbreak of the pandemic has a very huge impact on the check in rate. Especially during the lockdown period, check in dropped sharply, but after lockdown terminated at the end of October, check in appeared huge rebound.
Price relation analysis


No particular trend in prices over time can be seen from the chart both in mean and median.


Above we plot the meadian price distribution,next we will show price range for different room type.




Entire home / apt and hotel has much higher median price than others.
Features analysis which affect the popularity of room

From The following interactive chart, it shows price and location will impact if a room is popular or not. Popular room’s price usually below 500, secondly, when we hover over the scatter, we will show the area where the corresponding point is located, and find out whether it is in the urban area is also an important factor affecting the popularity of the house;Popular room’s the location is not far away form city.
Sydney area futhermore analysis
Next,based on previous analysis, Sydney City area has the largest market share. We will do some analysis based on this area.

1 bedroom make up the majority of listings

Entire home/apt , hotel room and Private room have much higher price
than Shared room.
Then we are curious about whether there exists price trend in these
select feature(Sydney city, entire home/ apt, 1 bedroom)?

We find no particular trend in prices over time can be seen from the
chart.
Then we conduct a host relation analysis-Changes in the number of hosts
settled and listings in Airbnb in Sydney over time.


From the above chart, from 2014-2016, hosts settled in Sydney airbnb
expand rapidly. From 2017, growth of new hosts settled become slowly,
but listings still increase fast,especially in 2023
Why is there an increase in listings when there are fewer new hosts?

Some hosts hold a large percentage of the market share from the above analysis(such as MadeComfy), maybe that is why from 2017, the host increase slow, but the number of listings still growth fast.

Here is business growing trend among almost Top3.This confirms the previous findings,although the total number of bookings is relatively stable, this trend is still preserved:from 2014-2016, hosts settled in Sydney airbnb expand rapidly. From 2017, growth of new hosts settled become slowly.
Trend Analysis
In this section, we will analyse the demand for Airbnb listings from the dataset. We will look at demand over the years since the inception of Airbnb in 2009 and across months of the year to understand seasonlity. We also wish to establish a relation between price and demand. The question we aspire to answer is whether prices of listings fluctuate with demand.We will also look at how prices change and fluctuate in different months of the year. To study the demand, since we did not have data on the bookings made over the past year, we will use ‘number of reviews’ variable as the indicator for demand. As per Airbnb, most of guests review the listings, hence studying the number of review will give us a good estimation of the demand.
How popular is Airbnb?

The number of reviews for Airbnb listings has shown a significant exponential increase over the years, indicating a substantial rise in demand since Airbnb’s inception in 2009. This growth suggests that the platform has become increasingly popular among travelers.

In this graph, the data for different years are represented by different colors. One can observe that number of reviews/demand also depicts a seasonal pattern. Every year there are peaks and drop in the demand, indicating that certain months are busier compared to the others.
Let us look at monthly demands for each of the years.






Trend Plot






Trend Plot
Demand for Airbnb listings is not uniform throughout the year. There are noticeable seasonal patterns, with certain months experiencing higher demand. For instance, the data indicates that demand is generally lower in the middle months of the year and increases towards October. This seasonal fluctuation can be linked to several factors:
-
Tourism Seasons: In regions where tourism is seasonal, demand for Airbnb listings spikes during peak tourist seasons. For example, spring and winter might be more popular due to favorable weather conditions and holiday seasons.
-
Holiday Periods: Months that include major holidays, such as December with Christmas and New Year’s, see higher demand as people travel for vacations and family gatherings.
To mathematically validate the initial observations, a time series analysis was conducted on the review data.
Step I:Time Series Decomposition
-
Trend Component and Seasonal Component: The trend component extracted from the time series decomposition indicates a consistent increase in the number of reviews over time, and The seasonal component reveals regular patterns that repeat annually
-
Residuals: The residuals show the remaining variability in the data after removing the trend and seasonal components.

Step II:Autocorrelation and Partial Autocorrelation
To further understand the underlying patterns, autocorrelation (ACF) and partial autocorrelation (PACF) functions were plotted. These plots help identify the dependencies between observations at different lags.

Step III:ARIMA Model
An ARIMA (1,1,1) model was fitted to the time series data to capture the autoregressive and moving average components.
-
AR(1) Coefficient: 0.5401 (p < 0.001)
-
MA(1) Coefficient: -0.9637 (p < 0.001)
-
Model Summary

Step IV: Forecasting Results
The forecast from the ARIMA model aligns well with the original data, capturing the upward trend and seasonal fluctuations.

The time series analysis confirms the initial conclusions drawn from visual inspection. The number of reviews for Airbnb listings has been increasing exponentially, reflecting growing popularity. The seasonal decomposition and ARIMA model provide a robust mathematical validation of these trends and seasonal patterns, further supporting the observation that Airbnb has become a preferred accommodation choice for travelers worldwide.

This pattern is also reflected in the availability of listings, with the number of unavailable listings (indicating booked properties) increasing during high-demand months. In above figure, the orange parts show the number of monthly unavailable listings and the green parts show the number of available listings, which also confirms the above conclusion from month to month
How is Airbnb priced across the year?
Let’s start by drawing the monthly average listings price curve for each year in one figure and try to find the trend.

One year the price curve was too curved, so the overall picture is not significant.So we try to calculate the average curve for each year. On the other hand, this means price fluctuations will not be particularly large generally

The pricing of Airbnb listings also shows distinct trends throughout the year. By analyzing the monthly average listing prices for each year, we observe:
-
Lower Prices in Mid-Year:
-
Price Increase Towards Year-End:
-
Volatility and Stabilization:
The correlation between price and demand is evident but not very strong. And then we’ll test that claim mathematically.
Part I:ANOVA Analysis
To further analyze the price volatility across different months, we conducted an ANOVA test to determine if there are significant differences in listing prices across months. The results showed significant differences in prices, indicating that the month of the year does impact Airbnb listing prices.


The boxplot above, with outliers removed, visually confirms the significant differences in prices across months, with notable peaks and troughs aligning with holiday seasons and tourist patterns.
Part II:Time series Analysis
We also performed a time series analysis to observe the impact of seasonality on Airbnb listing prices. By decomposing the time series into trend, seasonal, and residual components, we observed the following:


The seasonal component clearly shows recurring patterns within the year, indicating higher prices during certain months (e.g., peak holiday seasons) and lower prices during off-peak months.
Part III:Rolling 12-Month Standard Deviation:
The plot of the rolling 12-month standard deviation shows the changes in price volatility over time.

Periods with a higher rolling standard deviation indicate greater price volatility, while periods with a lower rolling standard deviation indicate less price volatility. Below is the result of Augmented Dickey-Fuller (ADF) :
-
Test Statistic: -1.8739
-
p-value: 0.3444
-
Critical Values:
-
1%: -3.5079
-
5%: -2.8954
-
10%: -2.5848
-
The ADF test results show that there is no significant downward trend in price volatility.
Geographical location analysis
This part presents a detailed analysis of location visualization and various neighborhood characteristics. The study includes a comprehensive examination of house number distribution, price analysis, review scores, and room type distribution across different neighborhoods.
Neighborhood Analysis
Figure illustrates the distribution of house counts across different neighborhoods. The color intensity varies according to the house count, with darker colors representing higher counts.

The figure shows that 21 neighborhoods are included. The average house count across these neighborhoods is around 47. The smallest neighborhood consists of 3 houses. While 75% of the neighborhoods contain 46 or fewer houses, the neighborhood with the maximum number of houses is Sydney, which has significantly more than the others.
Here I use the Folium package in Python to create an interactive map. This map visualizes the distribution of housing listings across the city. Cluster Map
The map provides an intuitive way to understand the spatial distribution of properties and identify areas with high or low densities of listings. The interactive map clearly reveals a significant concentration of houses in Sydney, evidenced by the large number of clusters in this area. Users can click on any area of interest to zoom in and view the detailed distribution of housing listings within that specific geographic region. This functionality allows for an in-depth exploration of the spatial patterns and densities of listings.
Price Distribution Analysis
In this part, a One-way ANOVA was initially conducted to analyze the price differences across various neighborhoods. However, the test revealed that the homogeneity of variance assumption was not satisfied(p-value < 0.05), indicating that the variability in house prices is not consistent across all neighborhoods.

Due to the failure of the homogeneity of variance in the One-way ANOVA, a Kruskal-Wallis test was conducted. This non-parametric test does not assume equal variances and is suitable for comparing price distributions across multiple neighborhoods. The results provided a more reliable comparison of house prices, identifying significant differences between neighborhoods. You can see in the Figure below:



The boxplot(Price Distribution By Neighborhoods) illustrates the distribution of housing prices across different neighborhoods. We can find that Sydney shows high variability with a large number of outliers, indicating a wide range of housing prices. The median price is relatively high. Besides, Mosman and Hunters Hill also exhibit significant variability and a high number of outliers, suggesting diverse property values. Fairfield and Camden have lower median prices with smaller IQRs, indicating more uniform and lower-priced properties.
From Wilcoxon score Figure, we could compare each neighborhood’s scores to expected values under the null hypothesis (H0). There are some notable findings:
-
Sydney: Has the highest sum of scores (185254.00) and mean score (643.24), reinforcing its status as a high-value area.
-
Mosman and Woollahra: Also have high sum and mean scores, indicating premium property values.
-
Fairfield and Camden: Lower sum and mean scores align with their lower housing prices.
The Kruskal-Wallis test evaluates the differences in housing prices across neighborhoods, considering the non-parametric nature of the data. These results indicate a statistically significant difference in housing prices across neighborhoods (p < 0.0001). The boxplot of Wilcoxon scores agian strongly supports the above analysis.
In order to more intuitively understand the changes of price with regional distribution, I obtained the geographical data of Sydney neighborhood from the Internet and combined it with the data set in our paper to draw the interactive heat map of average price in various regions: Average Price Per Neighborhood.
You can observe that the most expensive neighborhoods—Mosman, Woollahra, Sydney, and Willoughby—are all bay cities. These areas benefit from stunning sea views and convenient transportation links, which significantly enhance their attractiveness and desirability. As a result, average house prices are much more expensive than elsewhere.
Room Ratings Distribution Analysis

Similar to the idea of analyzing the price distribution, we first conducted one-way ANOVA analysis and found heteroscedasticity, and then conducted Kruskal-Wallis test.

By analyzing the review score distributed with neighborhood, we find that the score of certain neighborhoods fluctuates significantly. For example, Sydney, Fairfiel and burwood have many listings with low evaluation. This lowers the average rating in the region. Other cities (e.g. Camden, Canada_B, Willough) have relatively high and stable ratings, with few unusually low ratings recorded.
The analysis of ratings by neighborhood reveals substantial differences in satisfaction levels across the city. High-ranking neighborhoods like Woollahra, Waverley, and Willoughby show consistent positive feedback, whereas areas like Blacktown and Burwood exhibit more variability and lower ratings. The Kruskal-Wallis test further confirms that these differences are statistically significant with p-value < 0.0001.


Along the same lines as above, I draw the specific distribution of houses with different ratings on the map, and the rating scale transitions from the highest dark green to red below 3.0 (need to pay attention to the location of lightning protection). The details can be seen in the legend of this html file. Ratings Distribution Map
At this point, we can merge the two geographical analyses of prices and ratings to simultaneously reach a meaningful conclusion:
-
Sydney: High property values and consistent high ratings reflect its comprehensive advantages, international appeal, and strong infrastructure.
-
Woollahra:Combines affordability with high ratings, underpinned by a strong community environment and quality services.
-
Mosman: Balances high property values with high satisfaction ratings, offering a high quality of life in affluent surroundings.
Room Type Distribution Analysis
The bar chart illustrates the distribution of different room types across various neighborhoods. The room types are categorized as Entire home/apartment, Private room, Hotel room, and Shared room, each represented by different colors.
The room type distribution analysis reveals that entire homes/apartments are the most prevalent type of accommodation across most neighborhoods, particularly in Sydney and Mosman. Private rooms also have a significant presence in several neighborhoods, indicating a diverse range of accommodation options. In contrast, hotel rooms and shared rooms are less common, suggesting specific market preferences or regulatory influences in these areas.

As before, I also visualize a map of room type distribution: Room Type Distribution Map.
Two-Way ANOVA Analysis of Influencing Factors on Housing Prices
We are keen to understand the influence of room type and neighborhood on house prices. As such, we will use multi-factor analysis to investigate this topic in this section.
This analysis utilizes a General Linear Model (GLM) to examine the influence of neighborhood location and room type on housing prices. The table provides a detailed breakdown of the ANOVA results, including the effects of location, room type, and their interaction on housing prices.
-
Room Type: The room type has a significant effect on housing prices (p < 0.0001), indicating that different types of rooms command different prices.
-
Location: The initial analysis (I Type SS) suggests that location significantly affects housing prices (p < 0.0001). However, after controlling for other variables (III Type SS), the effect of location on price is not significant (p = 0.0806).
-
Interaction: The interaction between location and room type is not significant (p = 0.8717), suggesting that the combined effect of these factors on housing prices is not different from their individual effects.



This analysis highlights the importance of room type in determining housing prices and suggests that while location plays a role, its impact is mediated by the types of rooms available in different areas.
2.Regression
Data Preprocess
First, we carefully clean the data to our desired format.

As the figure shows here,white means NA and black means normal data. We can see there are 14274 rows of data with 75 features, and lots of na. So first, I drop several features, including some descriptions, URLs, and IDs, which are useless for regression in the next step.
We drop: 'calendar_updated', 'neighbourhood_group_cleansed', 'host_neighbourhood','host_description', 'host_about', 'host_id', 'host_thumbnail_url', 'host_name','host_neighbourhood', 'host_url', 'id', 'license', 'listing_url', 'name','neighbourhood_overview', 'picture_url', 'source','host_since','last_scraped','host_picture_url','calendar_last_scraped', 'scrape_id', 'host_location','neighbourhood'
Then, I carefully convert some discrete data to ordinal or nominal number, do some shuffle and create some reasonable new features.
-
Host_response_time: base on response time ordinally convert it to 1,2,3…
-
House_vertifications: use one-hot to encode this feature, which means does the host has email or work-email or not.
-
Bathsrooms_text: base on whether this text contain private , public or not to construct 2 new boolean feature of ’private-bathroom’ and ’public-bathroom’.
-
Filter ’%’ , ’$’,’.’ in price and rate features to get float feature.
-
First/last_review convert to the timestamp for downstream analysis and subtract to get ’airbnbage’, which shows how old the listing is.
-
Get top 20 frequent items in the amenities, create 20 new boolean features of these items.
Here are top 20 frequent items in amenities:'Smoke alarm', 'Kitchen', 'Wifi', 'Essentials', 'Dishes and silverware', 'Hot water', 'Hangers', 'Hair dryer', 'Bed linens', 'Microwave', 'Iron', 'Cooking basics', 'Refrigerator', 'Shampoo', 'Hot water kettle', 'Self check-in', 'Toaster', 'TV', 'Long term stays allowed', 'Washer'
Then, I dropped Na and built dummy variables to other discrete features. Finally, we get 10256 rows with 71 features. Then I randomly reorder the data and split train-test data with 7:3, which 7179 train datas with 71 features.
After data cleaning, we want to predict the list’s ’number-of-reviews-l30’. It means the number of reviews a listing has received in the last 30 days. It shows the recent attractiveness and popularity of a listing, which is useful.Here is our pipeline.

Linear Regression
First, I directly make linear regression and do hypothetical test, get R2 = 0.748 and Adj**R2 = 0.745, however, I draw residuals-Fitted value plot and QQ plot and get bad result:


With Breusch − Pagantestp* − *value* = 3.223450077501935*e*−62,*Shapiro* − *Wilktestp* − *value* = 2.6064151436441598*e*−43,and *Durbin − Waston*:1.977, we figure out that for the assumptions: Linearity, Homoscedasticity, and Normality are all not satisfied. So we need to do further transformation. First, I use BoxCox transform y to follow a normal distribution. Then, I discovered that multilinearity exists, so I dropped variables with *VI**F > 10. Then, we detected outliers with three aspects: Cook’s distance, Leverage, and Residuals. I got a scatter plot below:

Based on the experiment, I find that only dropping high cook’s distance points will lead to better performance on test data. If we drop high leverage and high residual data too, we’ll get poor performance on test data. So we just drop the high cook’s distance data. Finally, we get a Linear Regression model with R2 = 0.820, AdjR*2 = 0.818 on filtered train data. We also try WLS to avoid Heteroscedasticity, with *R*2 = 0.954, *AdjR2 = 0.954 on train data.
However, we get poor performance on test data with R2 = 0.45 for WSL and R2 = 0.46 for linear regression. The plots below clearly show that all the assumptions are not satisfied.


So we try other regression models.
Other Regression
We try RandomForest(RF), XGBoost(XGB), Lasso, and Ridge with Hyperparameter Slction based on train data. First, we try to figure out which strategy is better when selecting a hyperparameter. We compare three popular ways: RandomGridSearch, HalvingRandomSearchCV, and Tree-structured Parzen Estimator(TPE). We use Cross-validation with k=5 as an evaluation for the model when selecting a hyperparameter.
First, we compare 3 hyperparameter-selecting strategies with RF. We select a hyperparameter on train data and evaluate the performance on test data; the result is below.

TPE performs best with the same iteration, so we choose TPE as the hyperparameter strategy.
RandomForest
After we get a quite good RF model, we can detect features significant by RF. Here are 20 important features from an RF perspective.

We find that:
-
Past data (reputation) will greatly affect recent performance
-
There exist location preferences
-
Shorter rentals - More reviews
-
Public ratings are important
-
Price is important
XGBoost
We also train a fine-tuned XGB with R2 = 0.846 on train data and R2 = 0.61 on test. Here are 20 important features from an XGB perspective.

We find that:
-
Past data (reputation) is important
-
Shorter rentals - More reviews
-
Public ratings are important
-
Facilities(bathrooms,iron) make sense
-
Customer Service(email, response-rate) is important
Lasso & Ridge
With TPE, we find the best α = 0.0001 with R2 = 0.55 on the train and R2 = 0.47 on the test. We can get the coefficient change with different α as below( just show 10 latest to 0’s coefficient)

Shows that Facilities, Past Performance, Rental, Service are the most important features.
With TPE, we also get the best α = 0.12, and R2 = 0.55 on the train data, R2 = 0.49 on the test data.
Fianlly, based on the analysis above, we can conduct:
-
Past performance(reputation) is important
-
Facilities is important(iron, enough bedrooms bathrooms etc.)
-
Service is important(response more frequently)
-
Short rentals bring more reviews
Recommendation system
This part we implement a content-based recommendation system for housing listings. Leveraging natural language processing (NLP) techniques and statistical analysis, the system aims to provide personalized recommendations based on user preferences and item features.
Content-Based Features Extraction
The recommendation system was designed using a content-based approach, focusing on various features of the housing listings.
Listings Features
-
Category Variables: Categorical features such as room type and host response time. We use label encoder to deal with them.
-
Continuous Variables: Numerical features standardized and cleaned to remove missing values.
-
Boolean Variables: Binary features indicating the presence or absence of specific attributes
To capture the semantic similarity between different listings, a Word2Vec model was trained on the text data from the listings. The parameter of model is:
-
Vector Size: 100 dimensions for each term, capturing nuanced meanings.
-
Window Size: 5, specifying the maximum distance between terms to consider for context.
-
Minimum Count: 1, ensuring that even rare words are included in the model.
-
Workers: 4, to leverage parallel processing and speed up training.
The Word2Vec model was used to compute text information vectors for each house listing. This involved tokenizing the text data and aggregating item features into a numerical representation that captures the semantic content of the listings.
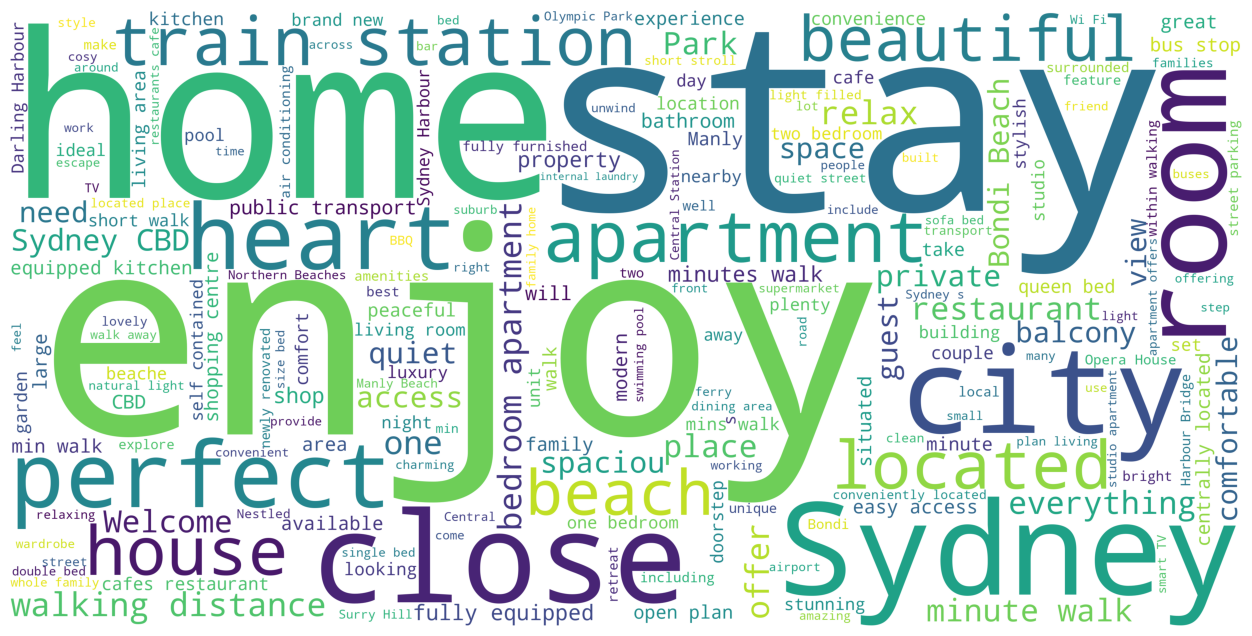
The cloud image of high-frequency words generated by listings text feature is shown as follows:

The most frequently occurring words in the names or titles of listings include: Apartment, Studio, House, Room, Home etc. These terms suggest a variety of property types can cater to different preferences and group sizes.
Other words related to locations, such as Sydney, Beach, Harbour, and Ocean View, suggest that many properties emphasize their proximity to water or harbor views, which are appealing features for visitors.

Guest expressions can be easily found as words like enjoy, perfect and beautiful etc. These words indicate that hosts focus on the overall guest experience, promoting a welcoming and enjoyable stay. Overall, the word cloud shows that Airbnb hosts in Sydney emphasize the comfort, convenience, and quality of their properties, highlighting key features and amenities.
User Feature
User features were derived from review comments and processed using the following resources:
-
NLTK punkt: For sentence segmentation and lexical segmentation.
-
Stopwords List: To remove common, non-informative words and focus on meaningful terms.
The average word vector was calculated for terms in the text data, representing the user’s preferences and interactions.
Recommendation Process
The recommendation system operates by calculating the cosine similarity between user features and item features. This similarity measure helps in identifying listings that are most similar to the user’s preferences.
Steps:
-
Given a Customer’s ID: Retrieve the recorded user features.
-
Cosine Similarity: Compute the similarity between customer features and item features.
-
Sorting: Sort the items in descending order of similarity.
-
Top K Items: Present the top recommendations to the user.
The content-based recommendation system effectively utilizes NLP techniques to personalize housing recommendations. By focusing on semantic similarities between user preferences and listing features, the system provides tailored suggestions that enhance user satisfaction and engagement.
Here is a demonstration of how our recommend system will work. Demonstration of Recommend System
Appendix
Code Repository:
The code is stored on GitHub
at https://github.com/YueWu0301/Airbnb_analysis
Website:
you can visit our project
via https://yuewu0301.github.io/Airbnb_analysis